2024 Small Business Entrepreneurs of Color
A Look at the State of Entrepreneurs of Color in 2024
In the ever-changing world of small businesses, understanding the experiences of entrepreneurs of color is not just beneficial — it’s imperative. Guidant reaches out annually to small business owners nationwide, gathering detailed insights into their challenges, successes, and aspirations.
This year’s study provides a deeper exploration into how election-year dynamics and political preferences are shaping the experiences and decisions of entrepreneurs of color, as well as assessing the broader economic effects on their businesses.
Supporting the success of underserved communities is fundamental for Guidant, especially for businesses operated by women and entrepreneurs of color. We are excited to disclose the trends and experiences of these entrepreneurs.
Index
What are Small Businesses Like in 2024?
Business Types
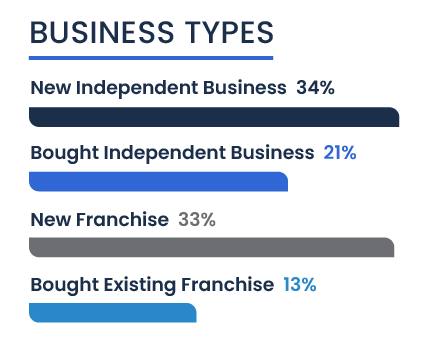
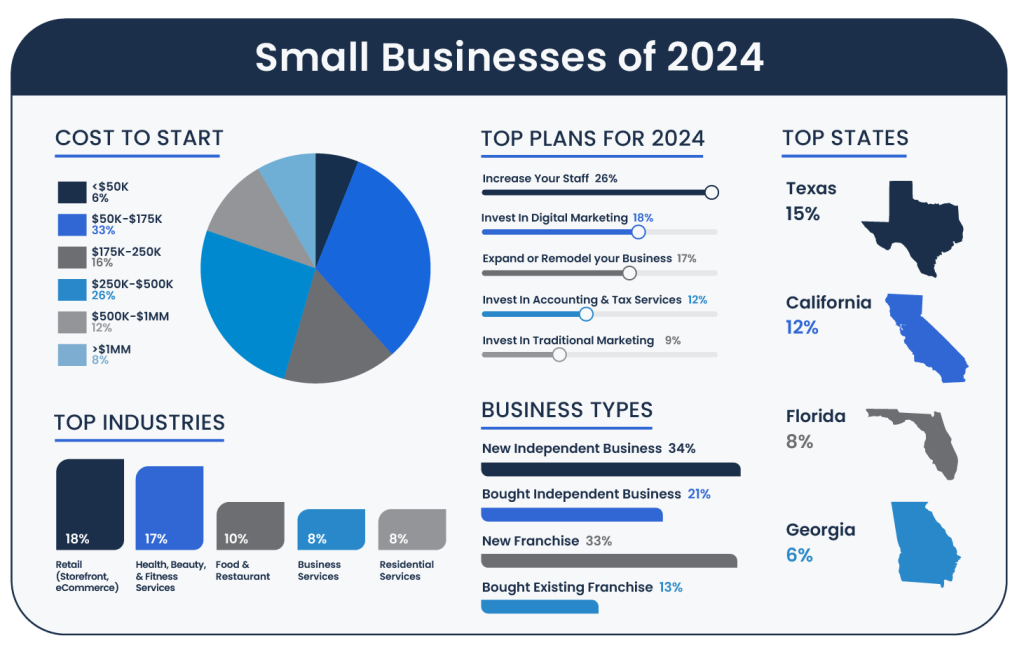
The data reveals a mix of entrepreneurial ventures: 34 percent of respondents have started new independent businesses, demonstrating a strong inclination toward building something uniquely their own. Another 21 percent are running existing independent businesses, indicating a stable presence in the marketplace.
Franchising also plays a significant role, with 33 percent of participants initiating new franchise locations attracted by the established systems and brand recognition. Meanwhile, 13 percent have purchased existing franchise locations, leveraging the continued success of proven business models.
Profitability and Growth
Profitability remains a challenge amidst inflation and high interest rates; although some businesses have managed to thrive post-COVID, many continue to grapple with achieving profitability as consumer spending lags. Notably, when excluding businesses that have been operational for only two years, only 56 percent are profitable, underscoring the ongoing struggle in this economic climate.
Despite challenges, 53 percent of businesses are currently reporting profitability. This figure is a testament to the resilience and determination of these entrepreneurs. The remaining 47 percent of businesses are not yet profitable.
Looking ahead to 2024, these entrepreneurs have laid out a variety of plans for growth, reflecting their optimism and strategic focus. Twenty-six percent of business owners plan to increase their staff, indicating confidence in expanding operations and scaling their businesses.
Digital marketing is another significant area of investment, with 18 percent of entrepreneurs aiming to enhance their online presence, which is vital for reaching broader markets in today’s digital-first economy.
Additionally, 17 percent plan to expand or remodel their businesses, while investments in accounting and tax services are a priority for 12 percent of the respondents. Lesser yet strategic investments include traditional marketing (9%), information services technology (7%), payroll services (7%), and technology to support remote work (4%). A small fraction (1%) is looking to outsource services to offshore companies, exploring cost efficiencies and global talent advantages to boost their operational dynamics.

Top Industries
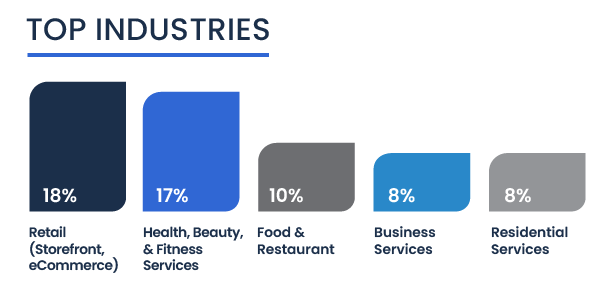
Meanwhile, residential/commercial services, construction/contracting, and business services each represent eight percent of the total, indicating a solid foothold in sectors that demand specialized knowledge and skills.
The variety in these sectors exemplifies how entrepreneurs of color are tapping into multiple opportunities to start and scale their businesses amidst fierce market competition.
Top Challenges
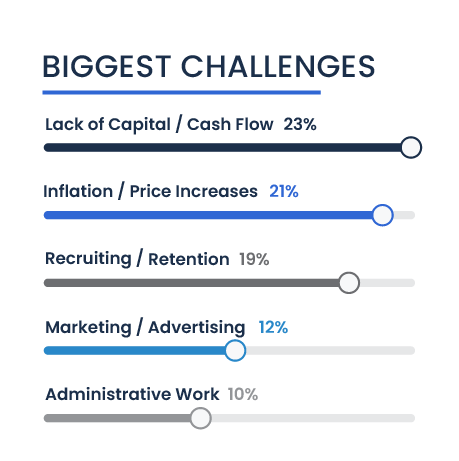
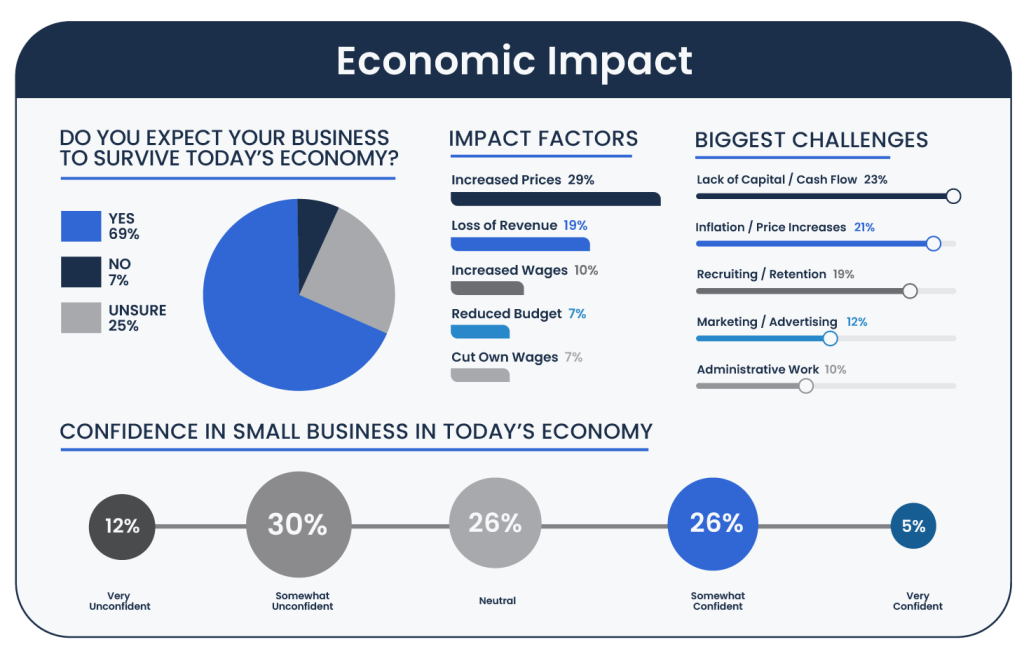
Recruiting and retaining staff is another significant challenge, affecting 19 percent of the participants, highlighting the difficulties in building and maintaining a reliable workforce.
Marketing and advertising pose a hurdle for 12 percent, indicating the need for effective strategies to enhance visibility and customer acquisition.
Administrative work and time management are also notable challenges, reported by 10 percent and six percent respectively, reflecting the operational complexities small business owners face.
Additionally , five percent each notes difficulties with supply chain issues and managing or providing benefits, pointing to the operational and employee management challenges in today’s economic landscape.
These challenges collectively depict the multifaceted difficulties entrepreneurs of color navigate as they strive to establish their foothold in various industries.
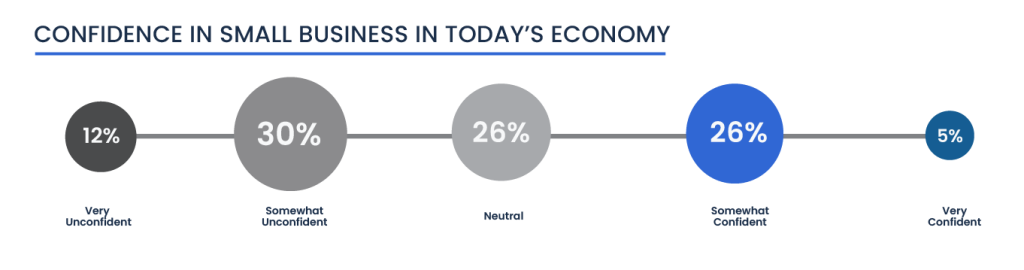
Economic Confidence
Recruitment and Retention
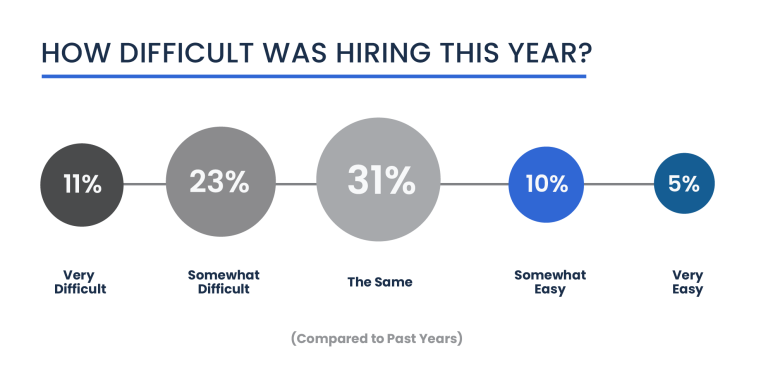
Regarding hiring difficulty, 11 percent of respondents find it very difficult, while 23 percent consider it somewhat difficult, cumulatively reflecting a significant challenge for nearly a third of the entrepreneurs. However, there’s a slight relief compared to last year, with a nine percent decrease in those who found hiring very to somewhat difficult.
The majority, 31 percent, report no change in the difficulty of hiring, while a minority finds it easier, with 10 percent considering it somewhat easy and five percent very easy.
In response to these recruitment challenges, entrepreneurs have adopted various measures to ease hiring difficulties. The most common strategy, implemented by 27 percent of business owners, is increasing compensation, aiming to attract more candidates and compete effectively in the labor market.
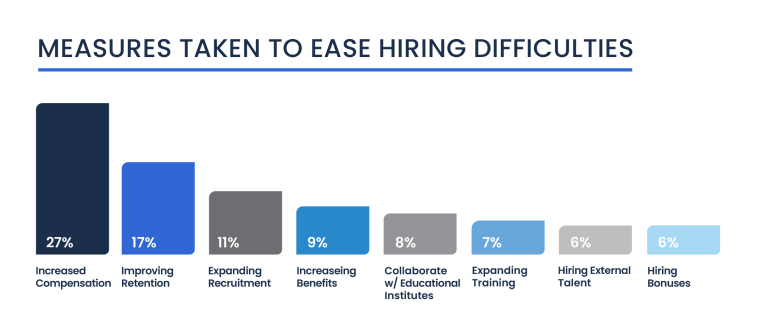
Improving retention efforts for current employees is also a key focus, with 17 percent enhancing practices to keep existing staff engaged and reduce turnover rates. Additionally, 11 percent have expanded their recruitment advertising to cast a wider net, and nine percent have increased employee benefits to bolster their value proposition to potential hires.
Other noteworthy measures include collaborating with educational institutions (8%), expanding training programs (7%), and offering hiring bonuses (6%). The adoption of remote work options and filling hard-to-fill positions with internal employees, both at four percent, also reflect adaptive strategies to address ongoing recruitment and retention challenges.
These efforts demonstrate the proactive steps taken by entrepreneurs of color to ensure they attract and retain the talent necessary to drive their businesses forward in a competitive market.
Who are Entrepreneurs of Color in 2024?
Motivations
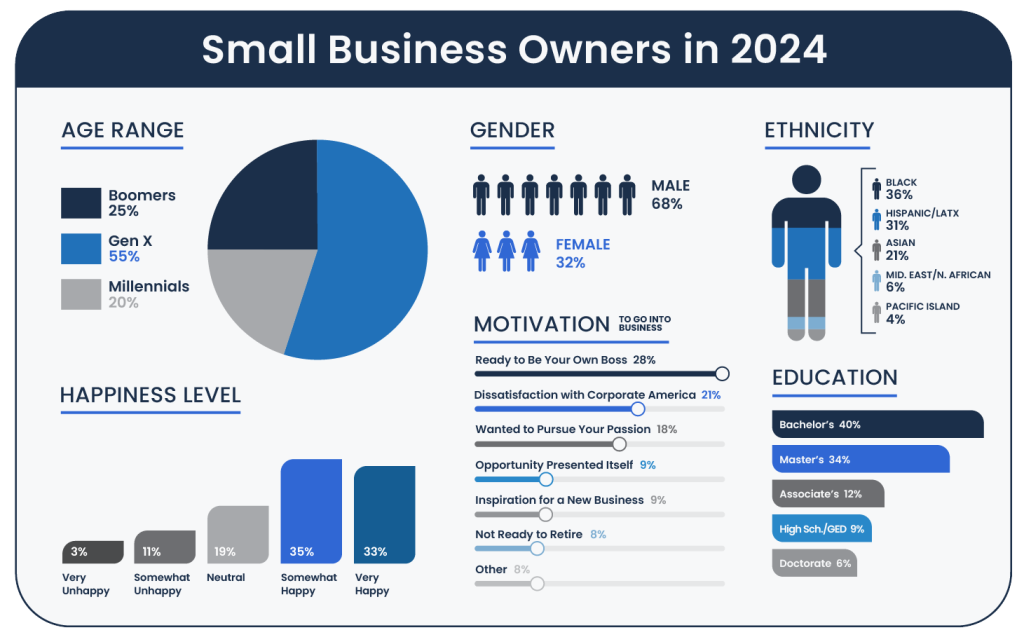
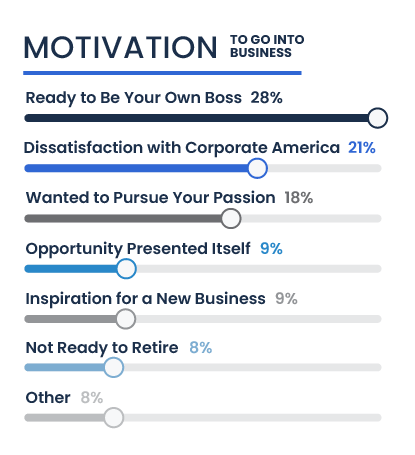
A significant 28 percent of respondents embarked on their entrepreneurial journey primarily to be their own boss, seeking autonomy and control over their careers. Dissatisfaction with corporate America also emerges as a notable factor, cited by 21 percent of the participants, reflecting a desire to escape the constraints of traditional employment settings.
Pursuing a passion motivates 18 percent, indicating that many are driven by the opportunity to turn what they love into a viable business. Additionally, nine percent each were motivated by an opportunity that presented itself or inspiration for a new business idea, showcasing how situational factors can spur entrepreneurial initiatives.
Other motivations include not being ready to retire (8%), being laid off or having their job outsourced (7%), and life-changing events such as divorce or the death of a loved one (1%), underscoring the diverse and sometimes challenging paths that lead individuals to venture into business ownership.
Happiness
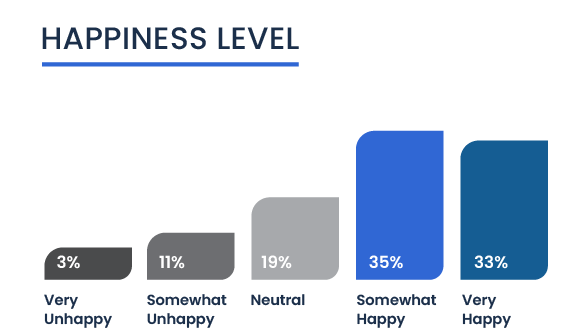
A majority of the surveyed entrepreneurs — totaling 68 percent — report feeling either somewhat or very happy. This suggests that many find rewarding aspects in their entrepreneurial journey, possibly due to successful business outcomes, strong community support, or personal fulfillment. Only a small fraction (3%) feel very unhappy, indicating potential struggles with issues like financial stress or barriers to accessing business resources.
However, the data also highlights that 11 percent of the entrepreneurs are somewhat unhappy, and another 19 percent feel neutral, neither happy nor unhappy. This subset may reflect those who face ongoing challenges or are still evaluating their satisfaction with their business ventures.
Age
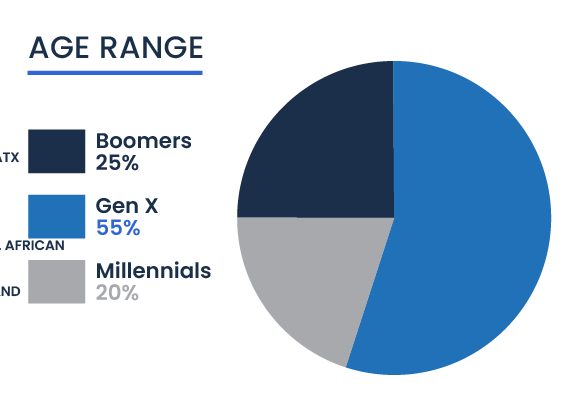
This indicates that Gen Xers are likely at a prime stage for entrepreneurship, benefiting from substantial experience and resources. Following are the Baby Boomers, making up 25 percent of the total. Millennials represent the smallest segment at 20 percent, yet they demonstrate a growing interest in entrepreneurship.
Trend analysis reveals significant changes over time in the age dynamics of entrepreneurs of color. Millennials have experienced a five percent increase in their representation, suggesting a burgeoning interest as more enter the age range conducive to starting businesses. Generation X has seen a nine percent increase, solidifying their strong presence in the entrepreneurial community. In contrast, there has been an 18 percent decrease in Baby Boomer entrepreneurs, aligning with broader demographic shifts toward retirement.
Diversity
The field of entrepreneurship within communities of color demonstrates substantial diversity, particularly observed in the variations of gender and race among entrepreneurs.
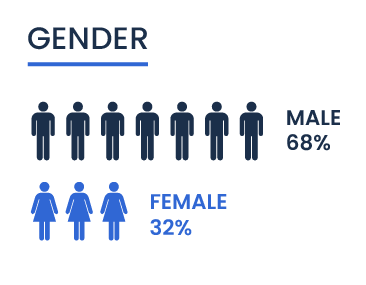
Gender distribution within this group shows a predominance of male entrepreneurs, who constitute 68 percent of the total. Females represent 32 percent, indicating a gender gap where men outnumber women more than two to one in entrepreneurial roles. This disparity highlights potential barriers that female entrepreneurs of color might face, such as access to capital, networking opportunities, and industry biases.
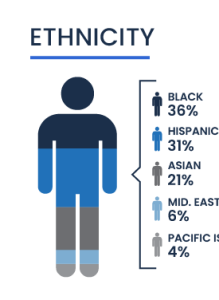
Education Levels
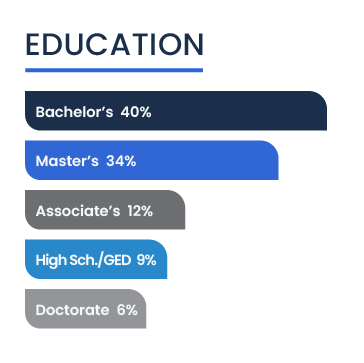
The educational attainment among entrepreneurs of color is notably high, with 40 percent holding bachelor’s degrees, reflecting a well-educated demographic within the community. This high level of formal education not only equips these entrepreneurs with essential knowledge and skills but also suggests a significant trend toward higher educational standards in the business sector.
Further analysis reveals that 34 percent of these entrepreneurs have master’s degrees, emphasizing the role of advanced specialized knowledge in entrepreneurship. Associate’s degrees and high school diplomas are held by 12 percent and nine percent respectively, showing that while higher education predominates, there is still a spectrum of educational backgrounds. At the top of the educational ladder, six percent possess doctorates.
Election Year Insights
Political Affiliation
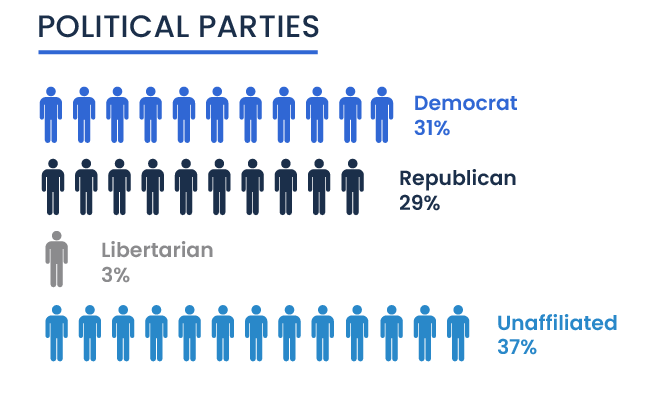
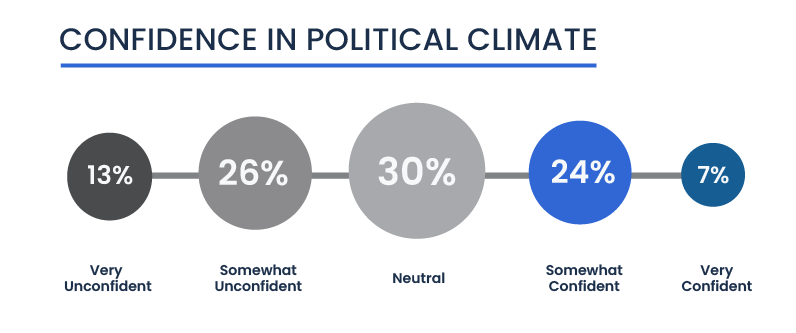
Political Confidence
Presidential Vote
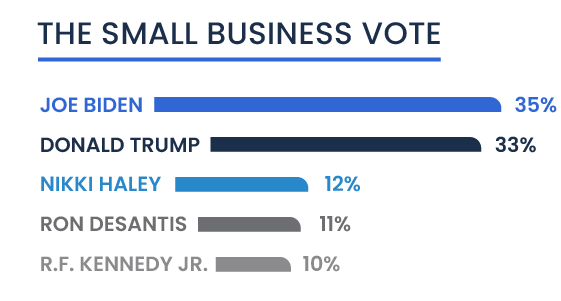
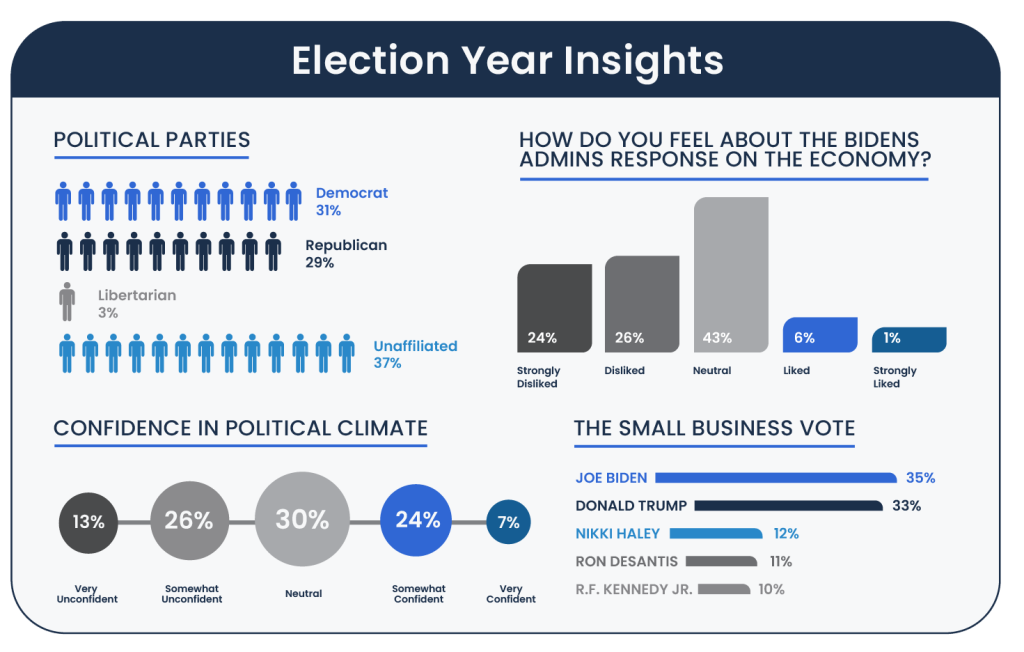
The poll also highlighted the presence of other significant figures in the race, with Nikki Haley receiving 12 percent of the vote. This indicates a notable faction within the entrepreneurial community that aligns with her political views and potential policy proposals. Ron DeSantis followed closely with 11 percent, suggesting his appeal among those looking for new conservative leadership. Robert F. Kennedy Jr. captured 10 percent of the votes, highlighting his influence among entrepreneurs of color who may resonate with his advocacy and perspectives. This data reveals the community’s multifaceted political preferences, mirroring a broad spectrum of values and priorities impacting their voting decisions.
Summary
In summary, the insights gathered from Guidant’s annual survey illuminate the complex interplay between political dynamics, economic conditions, and the entrepreneurial spirit among business owners of color.
This year’s findings are particularly poignant, reflecting the critical influence of election-year politics on business decisions and sentiments. Entrepreneurs of color are navigating these waters with resilience, despite facing unique challenges that differ significantly across demographics and industries.
Guidant’s commitment to inclusivity and support for underserved communities is more crucial than ever. By continuing to provide resources and advocacy, Guidant aims to play a pivotal role in ensuring that these entrepreneurs not only survive but thrive.
Trending
Your new life is right around the corner.
Together, we can get your business off the ground — no matter where you are in the small business process.